
Dhruva Das from Guwahati experienced frequent episodes of coughing, nasal congestion, and breathing difficulties when he was six years old. According to his mother, Mani Das, he also had a history of recurring ear infections, sinusitis, and snoring. She initially believed that her son was suffering from tonsillitis, but when her attempts to alleviate his symptoms with home remedies like salt and warm water gargles proved ineffective, she decided to take him to an ENT specialist.
Das was diagnosed with enlarged adenoid tissues (known as adenoiditis). “He was prescribed antibiotics and a few nasal sprays for one-two months, and he got better after that,” recalls his mother.
ABCs of adenoids
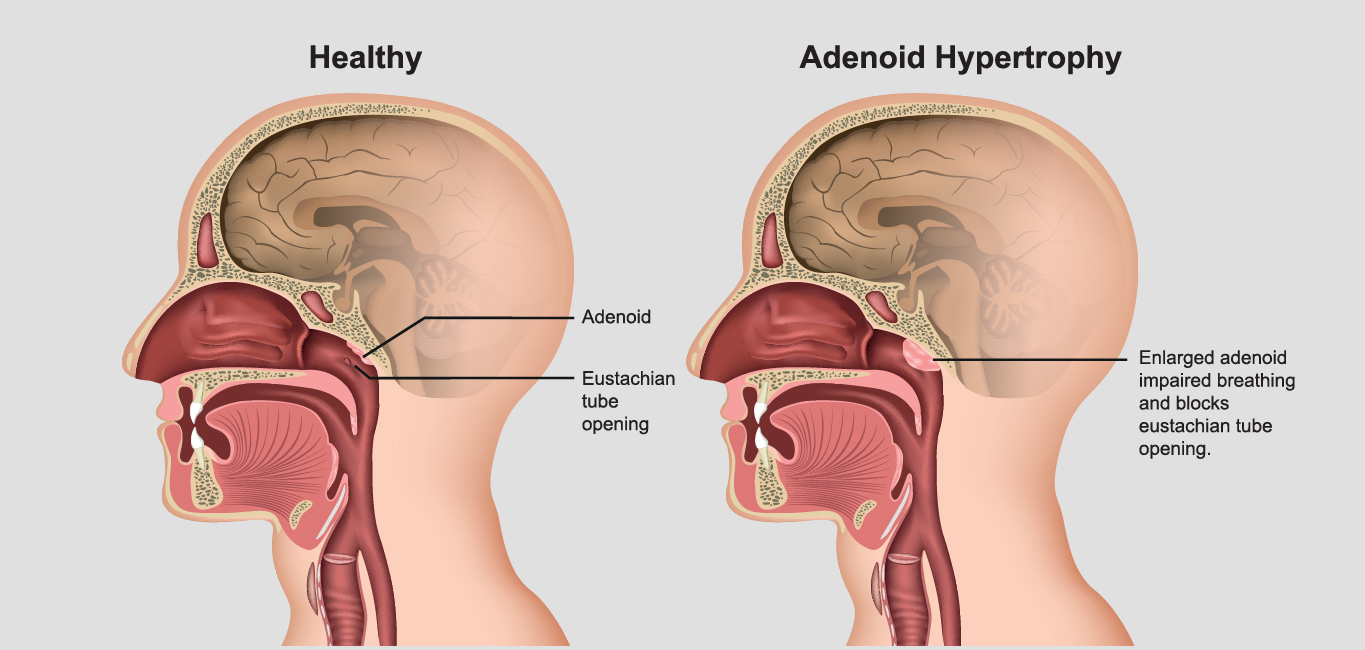
Adenoids are lymphoid tissues, also known as pharyngeal tonsils, which are situated at the back of one’s nose. An inflammation of these adenoids is known as adenoiditis, says Dr Sanjay Bhatia, senior ENT consultant, Fortis hospital, Mulund.
According to Dr Ria Emmanuel, ENT consultant specialised in allergy and immunotherapy, Narayana Multispeciality Hospital, Bengaluru, the types of adenoiditis are:
- Acute adenoiditis which lasts for a few days to a few weeks.
- Chronic adenoiditis lasts for months, and the inflammation can result in either infection, allergies, or irritation from stomach acids called laryngopharyngeal reflux.
Symptoms
“Adenoiditis rarely occurs on its own. So, it is usually seen as associated with extensive pharyngitis or rhinosinusitis,” says Dr Emmanuel. She further lists the symptoms based on different factors:
- If it is associated with pharyngitis then the person will have a sore throat, fever, pain, and redness locally in that region.
- If it is associated with rhinosinusitis, symptoms will be nose block, mucus discharge from the nose, facial congestion, and headache.
- Chronic irritation of adenoids can lead to adenoid enlargement that can block that region of the nose. This can cause Eustachian tube blocks, otitis media and otitis media with effusion (collection of fluids in the middle ear space). They can result in nose block, snoring and sleep-related breathing issues such as obstructive sleep apnea.
Causes
According to Dr Emmanuel, there are the three causes:
- Infections: Pathogens already present in the adenoids and tonsils can work synergistically to cause mixed infections. These can be airborne bacteria or viruses, or their chronic colonies that are already present in that area. Some common viral pathogens are Coxsackie, herpes, and Epstein Barr Virus.
- Allergy: Allergens like house dust mites, pollen, pet dander, and insect particles can cause adenoiditis.
- Acid reflux: Laryngopharyngeal reflux (a condition where stomach acid travels up the oesophagus and reaches the throat) is another cause of adenoiditis.
Diagnosis
“Nasal endoscopies are the preferred method of investigation, as they allow experts to see the tissues at the back of the nose using light passed through the nose,” says Dr Emmanuel.
While nasal endoscopy is an investigation of choice, some children might be hesitant. In such cases, it is advised to take an x-ray of the top part of the throat. If there are other complications such as sinusitis, then CT scan of the paranasal sinuses (one of the tiny hollows in the bones surrounding the nostrils) can be done.
If one observes chronic pus or post-nasal drip from that area, it may be appropriate to perform a swab culture to determine the appropriate treatment.
Treatment
According to Dr Emmanuel, treatment is based on the causes. For example, experts treat an infection with antibiotics and nasal sprays.
“If it is an allergy, experts try to find out the allergen that triggers their allergy and ask the individual to avoid it and use nasal washes with saline,” says Dr Bhatia.
In case of acid reflux, experts advise lifestyle modifications with diet, proper sleeping postures, and some medications to control it.
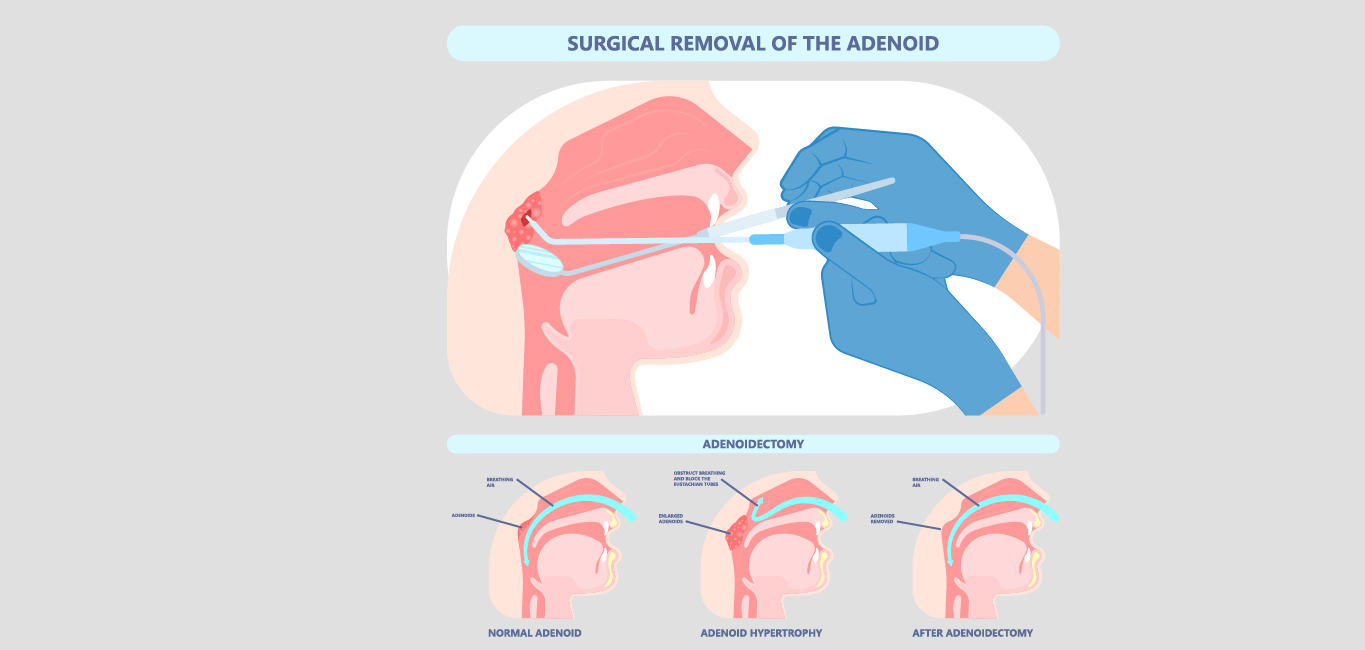
Adenoidectomy
According to Dr Emmanuel and Dr Bhatia adenoidectomy (adenoid removal) is advised when one has:
- Recurrent or multiple infections in a year (five to six times).
- Complications due to adenoids like recurrent sinusitis or otitis media or otitis media with effusion.
- Snoring and sleep apnoea.

















One Response
Very informative.