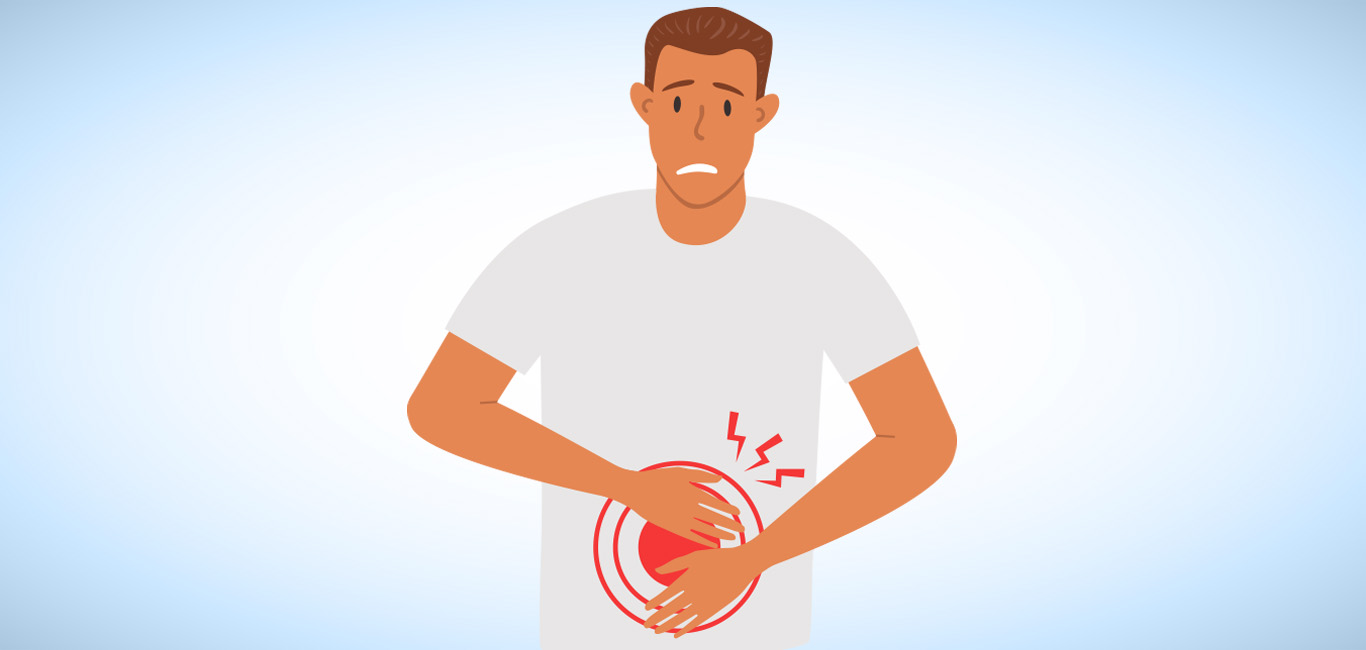
A hernia is a condition where an internal organ or tissue protrudes through a gap in the peritoneum (a muscular wall that keeps abdominal organs in place) or any weak muscle, most commonly in the groin region or the abdomen.
Hernias can be either internal or external when the mass of tissue is a visible swelling in the region.
Hernias are of different types:
- Inguinal hernias are common in men. Fatty tissues or parts of the bowel are swollen near the groin
- Femoral hernias are protrusions of fatty tissues of the intestine near the groin. They are often seen in women
- Umbilical hernias are frequently seen in infants wherein a portion of the intestines juts out through the belly button
- Hiatus hernia can occur when a portion of the stomach pushes up into the chest through a hole in the diaphragm. The diaphragm is a thin muscle that separates the chest from the abdomen
- Incisional hernias occur when an organ or mass of tissue pushes through a scar after surgery
Symptoms
Depending on the location and size, these are the most common symptoms.
- A visible swelling or a lump in the abdominal region or groin which disappears on lying down
- A shooting pain and burning sensation when lifting objects, exerting pressure, or coughing
- Occasional vomiting and constipation
A hiatus hernia can cause heartburn, acid reflux and pain in the stomach or chest. When it gets worse, there is difficulty in swallowing.
With inguinal hernia, there may be weakness, pressure around the groin, and pain around the testicles.
In children, the swelling from an inguinal hernia is normally smooth and painless. The lump is larger and easily visible when the child cries, coughs or strains, and may disappear when the child is lying flat.
Umbilical hernias in children appear as a soft swelling around the belly button. Upon exertion, the lump gets more visible.
Some symptoms require immediate medical attention:
- When the lump or the protrusion becomes soft, or changes colour to red or a darker shade
- If the lump cannot be pushed back or does not change size in a crying child
- If the person has fever, vomiting and severe abdominal pain
- If the person has bloating, difficulty in passing stools or inability to pass flatus
Causes
For a hernia to occur, there has to be a lot of pressure and an opening or a weak spot in a muscle, through which the organ or tissues can get pushed out.
- A hernia can be present at birth
- Sometimes an incisional hernia can appear a few months after abdominal surgery due to weight gain or pregnancy. It gets visible when there is pressure on the abdomen, such as during bowel movement or while lifting heavy weights
- Weak abdominal muscles can rupture over time and cause a hernia
- Most commonly, hernias occur in obese people, or in those who lift heavy objects, or during pregnancy. People affected by chronic cough, or sneezing, heavy smokers and those who have conditions like constipation or diarrhoea, can be affected by hernia. In all these instances, the abdomen is subjected to more pressure than usual
Diagnosis
- Examination of the swelling, and palpation (pressing) are enough to diagnose a hernia
- This may be done while asking the affected person to cough or to stand up.
- Ultrasound scans can confirm the location, size and severity of a hernia
- Very rarely, the physician may advise a Computed Tomography (CT) scan or Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
Treatment
Often, the treatment is decided after ascertaining whether the hernia is large and painful. Some lumps cannot be pushed back and may cause severe pain. They are likely to cause bowel obstruction. Such cases may require emergency surgery.
Elective surgery may be chosen if the hernia affects routine activities of the individual; or if the symptoms worsen progressively.
Surgery will be deemed risky for people with poor health.
In a child, an umbilical hernia will heal by itself before the age of five. If this does not happen, surgery is needed.
In the case of a hiatus hernia,
- Medications like antacids prescribed by a doctor are tried first to relieve symptoms
- Lifestyle changes like weight reduction and avoiding activities that create pressure on the stomach will reduce pain
- The physician may recommend diet changes such as avoiding fatty foods, caffeinated drinks, chocolate and alcohol. It also helps to eat smaller and more frequent meals instead of fewer and larger meals
An incisional hernia will require laparoscopic or keyhole surgery.
Your doctor will suggest the surgical repair in individuals with inguinal hernia and large femoral hernia.
The surgery
Hernias can be surgically treated in two ways:
- In an open surgery, an incision or cut is made, and the lump is pushed back. Sutures are placed to aid in repair. The tissues are retained and kept in place by a mesh, which also helps to strengthen the region
- A keyhole or laparoscopic surgery involves many small cuts. Special surgical instruments including a camera are used to guide the tissue back in place
A small hernia will most probably be observed for any change in size over time.
Sources: