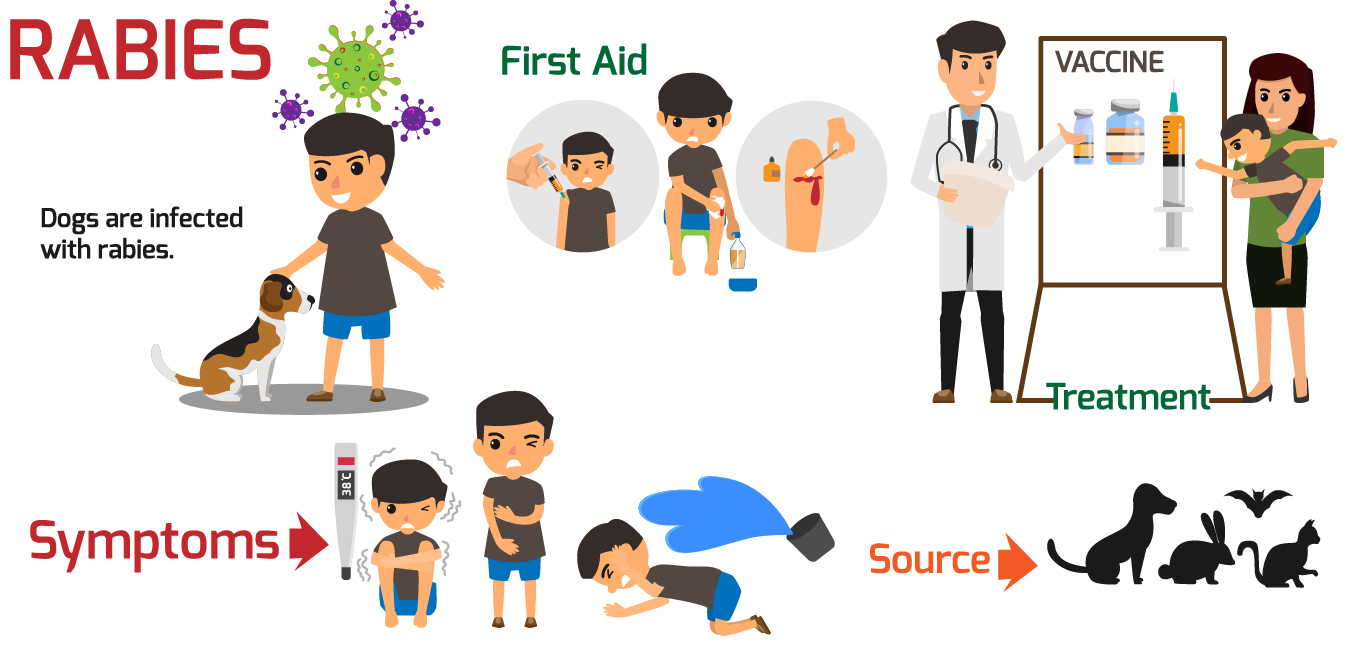
Rabies is a fatal but preventable condition caused by a virus that is usually transmitted to humans from the bite or scratch of an infected mammal, most often a dog.
The key to managing rabies is to get vaccinated soon after exposure to the virus.
Symptoms
The virus causes a serious infection of the nervous system including the brain. Once it enters the body, the rabies virus travels along nerves to reach the central nervous system (the brain and the spinal cord).
The condition passes through a few noticeable stages as the virus reaches the brain, causing different symptoms along the way.
The incubation period, from the time of entry of the virus to the first symptom, varies from one week to a year, depending on its mode of entry and the viral load. During this period, there is no risk of transmission.
There are a few general symptoms after the incubation, called the prodromal phase, when there is fever, pain, and a tingling or burning sensation at the site of entry or the wound.
Acute neurologic illness phase – When the virus enters the nervous system, it can present as either of two categories/forms of the condition-
Furious rabies or encephalitic rabies – The virus spreads from peripheral nerves to the central nervous system (brain) and returns to affect certain areas like the salivary glands. The patients show hydrophobia (fear of water) when swallowing liquids, and aerophobia (fear of fresh air).
Hydrophobia – There is intense frothing at the mouth due to hypersalivation, and spasm of the throat muscles at the mere sight or taste of water.
They exhibit agitation, neck stiffness, and breakdown of the autonomic nervous system, with increased heart rate, sweating, and difficulty in other functions. This is followed by hyperactivity.
Paralytic rabies or dumb rabies is less common and runs a longer course. Muscles are paralysed, usually starting at the wound site. There is fever, bladder dysfunction, and altered mental status.
About 10 days after the above stages, individuals with rabies enter the coma stage with flaccid paralysis, where there is a sudden weakness of muscles, and weakness in breathing and swallowing.
The final stage lasts for a couple of days, and almost all individuals die due to cardiopulmonary failure.
Causes
Rabies is caused by a virus that belongs to the rhabdoviridae family. It spreads by direct contact, mostly through the bite of infected domestic and wild mammals. The virus can also enter the body from scratches or licks on open wounds. Either way it is usually through infected saliva. Dogs are the main source of rabies in humans, but the rabies virus has been identified in bats, foxes, and raccoons.
Pets can be infected through contact with rabid animals. Humans can, in turn, get infected through such pets.
Diagnosis
It is difficult to diagnose rabies before the clinical signs appear. The characteristic signs of hydrophobia and aerophobia can be detected, and tests can be done to isolate the virus and detect antigens from saliva, cerebrospinal fluid, blood, or skin biopsy.
If possible, the biting animal may be euthanised and tested using direct fluorescent antibody test which can confirm the virus antigens in brain tissue. Treatment may be discontinued in case of a negative result.
Treatment
No effective treatment is available for rabies. Once the rabies virus manages to enter the brain, it seems to lock down the blood-brain barrier (BBB), a protective mechanism meant to prevent toxins from entering the brain. As a result, no medication has been able to cross the BBB to act against the virus.
Prevention is the only option, and it involves animal vaccination, and periodic monitoring.
In case a person has been bitten, or scratched by an animal that may have rabies, there is a protocol to be followed.
- The wound should be flushed with water and soap for 15 minutes
- Tincture or any iodine solution which acts against the virus should be used to wash the area
Post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP) – Starting the PEP prevents the virus from entering the central nervous system and causing almost certain death. The severity of the contact with the animal determines the PEP –
- Just touching or feeding animals, and animal licks on intact skin are categorised as no exposure and require only washing of the exposed skin
- If there has been nibbling of skin, or minor scratches even without bleeding, it is deemed to be exposure and requires wound washing and immediate vaccination
- If there has been severe exposure from single or multiple bites, or scratches or contamination of broken skin with saliva from animals –
– Rabies vaccine is given on the day of rabies exposure
– The vaccine is again administered on days 3, 7, and 14 as directed by the doctor
Protection against rabies
Rabies can be prevented by –
- Keeping pets away from wild animals, and not allowing them to roam without supervision
- Vaccinating pet dogs, cats and other domestic animals as per the protocol
- Not capturing or touching wild animals even if they are injured, and to rather inform concerned officials
Sources:
1.https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/rabies