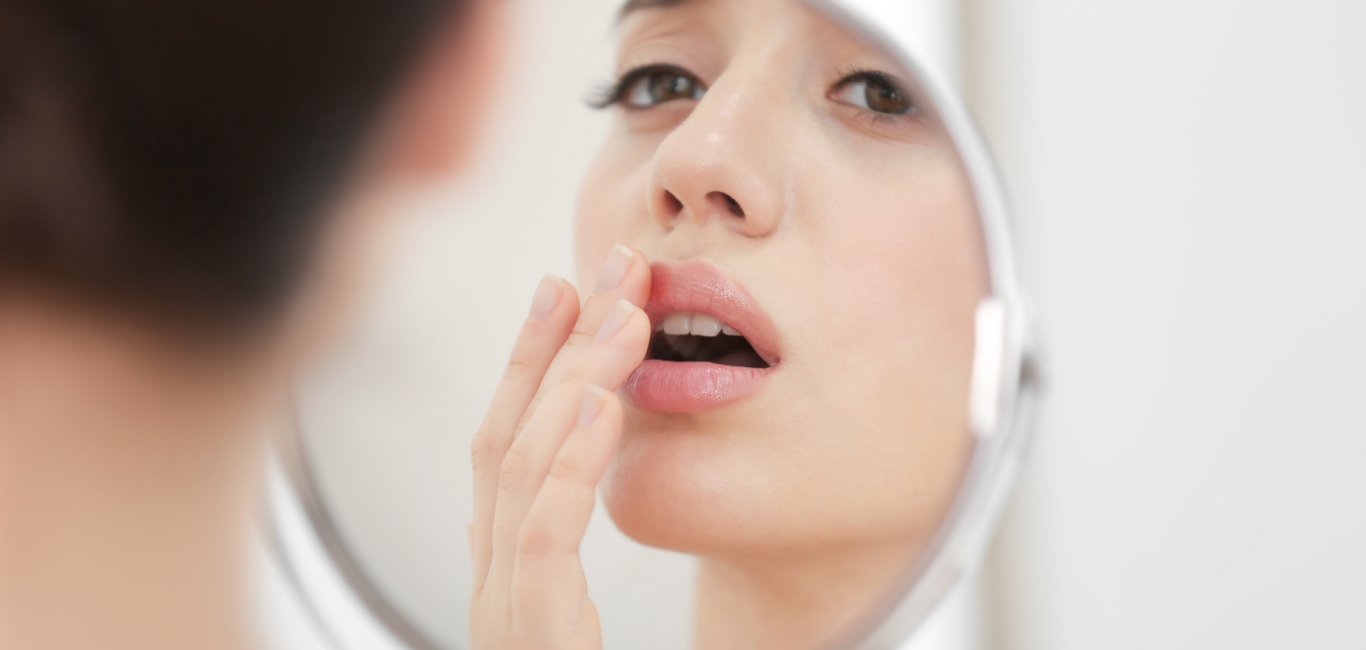
A cold sore is a collection of small blisters – tiny pockets of fluid just beneath the skin – which typically develop on the lips at the junction where the lips meet the facial skin. They may also form below the nose, on the roof of the mouth (palate), or over the gums around teeth. The blisters are red in colour, and quite painful.
They burst open after a few days, and fluid, which contains the virus, oozes out. A cold sore is very contagious from the time blisters are formed, till the sore is healed in about 10 days.
They are also called fever blisters or herpetic sores/lesions. Cold sores have an incubation period of 10-12 days from the moment of exposure till the symptoms appear.
Signs and symptoms
The infection can be annoying and have severe symptoms. Multiple sores can erupt and show symptoms like a flu. Subsequent infections tend to be milder or may not occur at all.
Some of the common symptoms associated with a cold sore are:
- A sore throat, and difficulty in swallowing
- A tingling or burning sensation in the specific spot before blisters form
- Redness and mild swelling before the infection erupts
- Painful blisters that appear at these spots, typically on the lips or under the nose and start discharging fluid
- Mild fever may accompany the blisters
- The gums may become swollen and turn reddish
- The glands in the neck (lymph nodes) may be enlarged, although the individual cannot feel them
Causes
Cold sores are caused by a re-activation of the herpes simplex virus (HSV). It usually infects people during childhood. It is primarily a skin disease that can be transmitted by touching infected skin, by kissing, or by sharing personal items like water bottles, shaving razors, lip balm, and so on.
There are two types of the virus:
- Herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV 1) that primarily affects the mouth and adjoining regions. This type is mainly responsible for causing cold sores
- Herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV 2) that usually affects regions below the waist. It is spread through sexual contact with a person who has a genital HSV 2 infection
Pregnant women with HSV 2 or genital herpes can also infect the baby during childbirth.
It is important to understand that both types can spread even in the absence of cold sores.
Though there is a stigma associated with a herpes infection, at any given time, either of the two types is usually present without symptoms in a vast majority of the population. Once it infects a person, the virus usually lies inactive within a bundle of nerve cells. It can get activated and cause periodic infections in certain people.
There are a few triggers that may re-activate:
- Prolonged exposure to sunlight
- Fever
- Some form of stress, sometimes post-surgery
- A compromised immune system due to conditions like AIDS
- Steroids or chemotherapy
- Menstruation
- Injury to regions that are usually affected by the virus
As the immune system develops antibodies to the virus after the primary infection, the severity of outbreaks becomes lower during every subsequent attack.
Diagnosis
Although a cold sore can be diagnosed by visual inspection and by noting the areas that are typically affected, HSV can be confirmed only by these methods:
- Virus culture from a swab of the tissue or fluid
- Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) tests that provide information about the type of virus, from a blood, fluid or skin sample
- A blood test to determine the presence of antibodies against previous infection
In the absence of cold sores or any other lesion, a blood test is done around a month after a suspected infection, so that antibodies that are formed can be detected.
Treatment & caution
Cold sores are self-limiting, they heal on their own in a couple of weeks. However, there is no cure for HSV infections, as the virus remains in the body in the dormant state after infection.
To help deal with the discomfort of large cold sores:
- Pain killers can be taken
- Gels or creams with local anaesthetics can be dabbed, but not rubbed on the cold sore. Some home remedies like ice packs over the blisters work well
- Anti-viral tablets may be prescribed to enable faster healing
- If the infection becomes severe as in medically compromised individuals, intravenous antiviral medicine may be needed
If HSV spreads to other organs, it may create complications.
- For instance, it can infect the cornea of the eye, which may lead to blindness
- It can lead to fatal conditions like meningitis, or encephalitis if it reaches the brain
It is important that persons with cold sores stay away from babies. Herpetic infections in new-borns can be fatal.
Sources: